The flat position signifies a fundamental form orientation by profound insinuations across multiple disciplines, including medical upkeep, physical therapy, fitness, and reintegration. Resulting after the Latin term “supine’s,” meaning deceitful on the spinal with the face rising, this location is critical in humanoid anatomy, healthcare, and therapeutic interferences. This complete guide will explore the complicated particulars of flat positioning, giving readers an in-depth understanding of its meaning, applications, and nuanced aids across numerous domains.
Keywords: passive location, body positioning, medicinal posture
Anatomical Understanding of Supine Position
Anatomical Mechanics
When an individual assumes a prone position, their body lies flat on the back, with the following key characteristics:
- Spine aligned in a neutral position
- Head resting on a surface
- Arms typically positioned alongside the body or resting on the abdomen
- Legs extended and relaxed
Physiological Responses
The prone position triggers specific physiological responses within the human body:
- Reduced gravitational stress on skeletal structure
- Enhanced blood circulation
- Decreased muscle tension
- Improved respiratory mechanics
Keywords: human anatomy, body alignment, horizontal positioning
Medical Applications of Supine Positioning
Keywords: medical positioning, patient care, diagnostic procedures
Clinical Diagnostic Procedures
Medical professionals extensively utilize the supine position during numerous diagnostic and therapeutic interventions:
Imaging Techniques
- X-ray examinations
- Ultrasound scans
- CT and MRI imaging
- Radiation therapy positioning
Physical Examinations
- Neurological assessments
- Orthopaedic evaluations
- Cardiovascular screenings
- Abdominal examinations
Surgical and Treatment Contexts
Surgeons and healthcare providers rely on supine positioning for:
- Surgical preparations
- Anesthesia administration
- Minimally invasive procedures
- Patient stabilization during treatments

Read more:Hypervigilance: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Overcoming Heightened Sensory Sensitivity
Supine Position in Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Keywords: rehabilitation techniques, physical therapy, recovery positioning
Therapeutic Benefits
Physical therapists strategically employ supine positioning to:
- Reduce joint stress
- Facilitate muscle relaxation
- Promote precise movement assessments
- Design targeted rehabilitation protocols
Specific Rehabilitation Applications
- Spinal Rehabilitation
- Alleviating lower back pain
- Correcting postural misalignments
- Implementing core strengthening exercises
- Neurological Recovery
- Stroke rehabilitation
- Nerve injury recovery
- Movement retraining techniques
- Orthopaedic Interventions
- Post-surgical recovery
- Joint mobility restoration
- Muscle re-education programs
Fitness and Exercise Considerations
Keywords: exercise positioning, workout techniques, body alignment
Exercise Modalities
The prone position serves critical functions in various fitness contexts:
Strength Training
- Core strengthening exercises
- Abdominal muscle development
- Resistance training techniques
- Pilates and yoga practices
Flexibility Enhancement
- Stretching routines
- Mobility improvement techniques
- Muscle tension release
Performance and Recovery
Athletes utilize supine positioning for:
- Post-workout recovery
- Muscle relaxation
- Injury prevention strategies
- Performance optimization techniques
Psychological and Comfort Perspectives
Keywords: body positioning, comfort techniques, relaxation
Stress Reduction
The prone position offers significant psychological benefits:
- Promotes relaxation
- Reduces anxiety
- Enhances meditation practices
- Supports mental health interventions
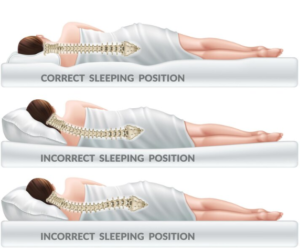
Sleep and Rest
Critical considerations for optimal rest:
- Mattress support requirements
- Pillow positioning
- Spinal alignment during sleep
- Pressure point management
Potential Risks and Precautions
Keywords: medical positioning risks, patient safety, body alignment
Medical Considerations
Healthcare professionals must evaluate:
- Individual patient conditions
- Potential pressure point complications
- Circulation limitations
- Respiratory function
Recommended Safeguards
- Regular position adjustments
- Pressure relief techniques
- Proper padding and support
- Individualized assessment protocols
Conclusion: Holistic Understanding of Supine Positioning
The prone position transcends simple body orientation, representing a complex interplay of anatomical, physiological, and therapeutic dynamics. From medical diagnostics to fitness applications, understanding its nuanced implications empowers individuals and professionals to optimize health, recovery, and performance.
As research continues to evolve, the significance of precise body positioning becomes increasingly apparent, highlighting the supine position’s versatile and critical role in human wellness.
Additional Resources
- Medical positioning guidelines
- Professional rehabilitation techniques
- Advanced physiotherapy approaches
Expert Consultation Recommendation
Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized guidance regarding body positioning and individual health requirements.
